The way customers use a product determines its performance. Often, minor flaws will cause them to reject and disappoint you.
Because we can have better user interaction in-store, it is easier to answer client's problems. It is not conceivable with a digital product.
A digital product will contain several flaws and errors, causing users to quit the site immediately. It is difficult to re-engage your users when there are fewer interactions.
So, what are the options? The use of feature usability testing may be a viable solution for locating difficulties.
We will cover the following:
- What is usability testing?
- 10 Reasons to use usability testing
- Methods of usability testing
- Usability testing vs User testing vs A/B testing
- How does usability testing work?
- How to conduct usability testing?
What is usability testing?
Usability testing involves putting a product through its paces with real users to see how easy it is to use.
Users are instructed to accomplish tasks and are monitored and examined by a researcher in an attempt to decide when they face difficulty and frustration.
Users have exactly the same issues. Fix these usability problems with these suggestions.
10 Reasons to use usability testing
- Identify every minute error.
- Verify that your product meets your customers' expectations.
- Determine the adjustments that are required to improve user performance and satisfaction.
- Find the Outcome results in satisfaction rating with each user, on user interference, and how engaging the product is.
- Examine the performance to evaluate if it meets your usability goals.
- Whether or not participants can effectively accomplish given activities.
- Test your model with users prior to deciding to fix the ultimate product to be released.
- Improve the user experience in order to gain more customers and boost your revenue.
- To determine the time required to perform given tasks.
- Evaluate how engaged participants are with your website or other offerings.
Methods of usability testing
In-Person:
Companies hire or use ordinary people and make them use their product and observe the outcome, and feedback, or do surveys to get what the users felt or if they had faced difficulty.
This is one of the traditional methods used by most companies.
These in-person usability tests are now quite old-fashioned. As of now, everything has changed. Technology has taken place.
But still, in-person usability testing is used for most of the products.
Guerilla testing:
Guerilla testing can be combined with both in-person and remote usability testing. When you ask any user to perform a task in return for any free sample or gift, then it is called guerilla testing.
Guerilla testing is done in a rapid time and also gives excellent results in return.
Remote:
Remote testing is done mostly in the software industry as it is easier to process.
Users are said to be in their own comfortable location and do testing.
As it is not done under an administrator’s eye, there is a high chance that people have not undergone testing and did the tasks well.
Unmoderated remote usability testing:
Test participants are requested to complete tasks in their own surroundings, with their own equipment, and without the presence of a moderator, resulting in the product being utilized organically.
Unmoderated testing is less expensive, but it provides fewer detailed testing findings.
Phone Interview:
A phone interview is a remote usability test in which a moderator vocally leads participants to do activities on their device while automatically collecting feedback.
Session recording:
Session recording is a technique for recording the actions of real but unidentified people while they engage with a website.
Session recording data aids in understanding what content is most appealing to consumers and what issues they encounter when interacting with the product.
Usability testing vs User testing vs A/B testing:
- Usability testing is when people try out a product's features and give a review of their experience.
- User testing is when you want to know that your product solves people’s difficulties.
- A/B testing is when you give two different interfaces to 50/50 website visitors and understand which interface optimizes more conversion rates.
How does usability testing work?
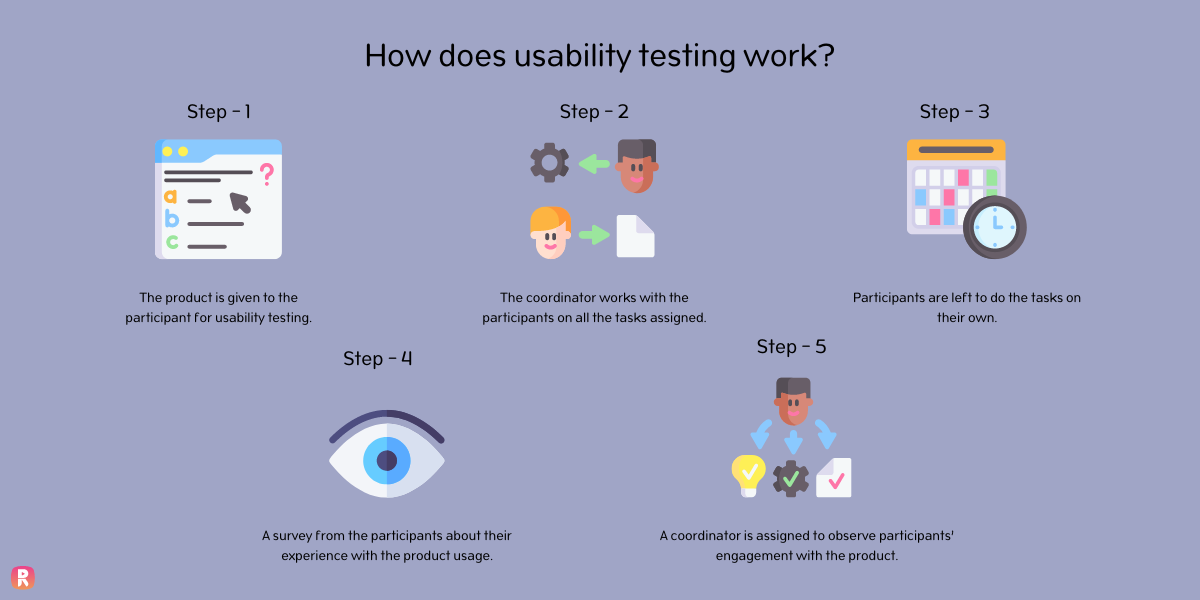
The four main components of usability testing are coordinator, participants, tasks, and product.
- Step 1: The product is given to the participant for usability testing.
- Step 2: The coordinator works with the participants on all the tasks assigned.
- Step 3: Participants are left to do the tasks on their own.
- Step 4: A coordinator is assigned to observe participants’ engagement with the product.
- Step 5: A survey or feedback session has to be conducted in order to get a review from the participants about their experience with the product usage.
How to conduct usability testing?
Various testing grounds are employed depending on the three categories of usability testing.
The tests that are carried out on a regular basis are highly beneficial in learning about the product that we have created.
1. Web usability testing:
The internet can be used to run tests remotely. Because the internet is now available worldwide, you may perform your tests and learn about the preferences of people from all over the world.
2. First click:
The first click assists you with navigating the website, as well as why and how visitors utilize it. There may be several parts, but you should be aware of the most crucial aspect of the website so that you can concentrate on it more.
3. Lab usability testing:
The entire research or testing is carried out in a laboratory setting. A sequence of tasks or questions would be assigned to the users or audience. You can determine the effectiveness of the product by evaluating its behavior throughout the test.
4. Eye-tracking:
The user engagement of a website is determined by the movement of the eye while using the digital product. The eye-tracking approach analyses each and every movement of the user in order to provide you with a detailed picture of their experience on the site.
5. Session recording:
This is a significant feature that website developers employ to examine visitor activity and behavior while on the site. Other options for session records include heatmaps and funnel analytics, which provide a full description of how the website works.
ReplayBird - Driving Revenue and Growth through Actionable Product Insights
ReplayBird is a digital experience analytics platform that offers a comprehensive real-time insights which goes beyond the limitations of traditional web analytics with features such as product analytics, session replay, error analysis, funnel, and path analysis.
With Replaybird, you can capture a complete picture of user behavior, understand their pain points, and improve the overall end-user experience. Session replay feature allows you to watch user sessions in real-time, so you can understand their actions, identify issues and quickly take corrective actions. Error analysis feature helps you identify and resolve javascript errors as they occur, minimizing the negative impact on user experience.
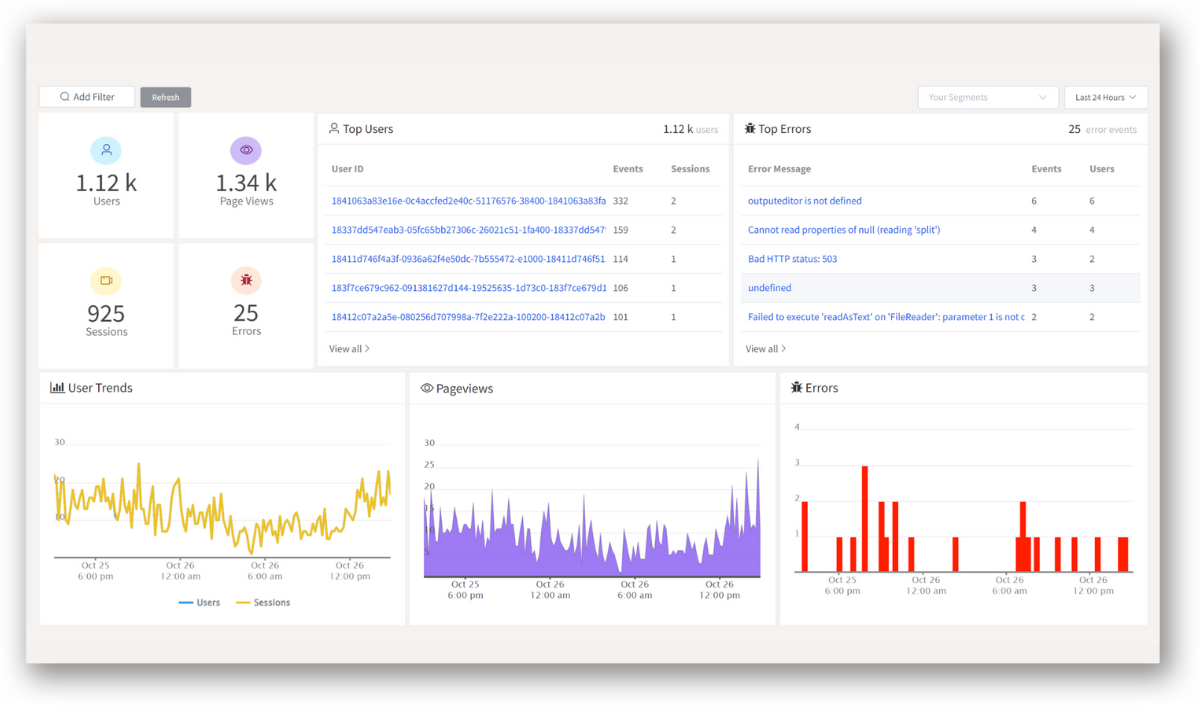
With product analytics feature, you can get deeper insights into how users are interacting with your product and identify opportunities to improve. Drive understanding, action, and trust, leading to improved customer experiences and driving business revenue growth.





