Everything around us is based on data. Data collection is a skill, whereas, in data research, the first abstract thing to learn is what its types are in order to know where to start your data collection.
Data is broadly divided into two types: quantitative and qualitative data. Both types are essential for any analysis or research.
Here are the topics we will cover in this blog:
- What is Quantitative Data?
- What is Qualitative Data?
- The Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Data
- Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Data in Example
- Which Type is Better for Data Analysis?
What is Quantitative Data?
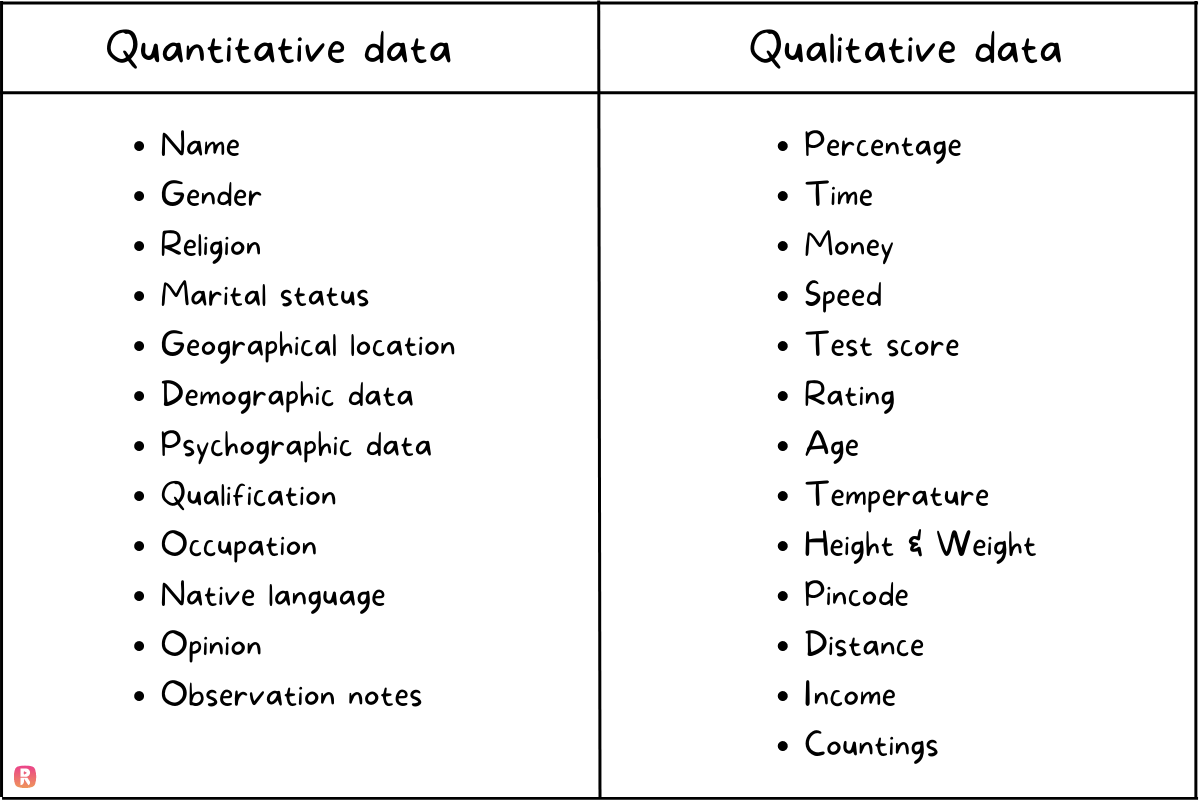
Quantitative data is data that is segmented into numerical variables. Data with quantity. Data that can be counted or listed is called quantitative data.
Quantitative data is used to justify theories and preconceptions. This qualitative research could be used to generate appropriate data about a subject.
Experiments, observations documented as statistics, and assessments with closed-ended questions are examples of standard quantitative procedures.
Furthermore, Quantitative data includes all numerical data such as time, the number of items, distance, lists, age, currency, money, metrics, calculations, percentages, and more.
Quantitative answers to the questions on:
- How many
- How often
- How much
- Total number of
- How long
- How far
Example of Quantitative Data:
- The score of one of the first-grade students was 99 out of 100
- Trees live up to 60 years
- The conversion rate of a good website is 3%
- The new model of the iPhone costs $999.
What is Quantitative Research?
Research and analysis of data that is numerical, which is all about collecting, interpreting, accumulating, measuring, and calculating.
The question can be answered using qualitative data. Quantitative is exploratory in nature and is frequently left open-ended when more research is undertaken.
This qualitative research data is utilized to generate hypotheses and preliminary conceptions, particularly through social interpretations and hypotheses.
Types of Quantitative Research Methods:
#1 Casual-comparative
Casual-comparative or quasi-experimental research compares two unrelated variables. One is dependent, and the other is independent.
It analyzes the cause-and-effect correlation among these factors to produce its results.
#2 Correlational
A correlational research design looks into correlations between variables without allowing the researcher to control or modify any of them.
A correlation is one of the best quantitative research methods that allow the measurement of the intensity and/or direction of a relationship between different variables. A correlation's direction might be both positive and negative.
#3 Experimental
Experimental research is a scientific inquiry that employs two sets of variables. The first set serves as a constant against which the differences in the second set are measured. Experimentation is used in quantitative research methodologies.
#4 Survey research
Survey research is a quantitative method in which a researcher asks a preset set of questions to a whole group, or sample, of people.
Survey research is particularly effective when a researcher wants to characterize or analyze the characteristics of a large group or group.
This approach can also be used to swiftly gather broad information on a population of interest in order to be ready for a more targeted, in-depth study using time-consuming methods such as in-depth interviews or field research.
What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data is more alphabetical and verbally explained. It is the descriptive and conceptual information gleaned from questionnaires, interviews, or observation.
By analyzing qualitative data, we can examine concepts as well as clarify quantitative outcomes. They can be categorized with identifiers, attributes, labels, and other meaningful language things.
Qualitative Answers to the Auestions on:
- What
- How
- Why
- Who
- Where
Example of Qualitative Data
- Product A yields more profit than product B.
- The color of the products has more impact on the customers than the
- Every customer gets a unique discount coupon.
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research does not give you a list or any calculation, but as it is alphabetical and verbal, you are competent to understand the category easily.
Qualitative researchers are important to accept how individuals build sense, that is, how their understanding of the world and the events they have anyway.
Qualitative research can be defined as research that employs methodologies such as observations, interviews, or case studies to produce a narrative, descriptive description of a situation or activity.
Sociologists who use qualitative research methods often reject positivism in favor of an interpretive approach.
Qualitative research is a situated activity in which the researcher is located in the world.
It is a collection of interpretative and material acts that make the place accessible. These activities have a positive impact on the planet.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
#1 Case study
The case study approach allows researchers to perform in-depth investigations of complicated systems within a specific environment.
With a research focus on experimenters, who work on their final dissertation, research students in any such discipline confront challenges in terms of clarity, choice, and successful implementation of qualitative case studies.
These challenges frequently create frustration, waste of valuable time, and poor decisions that have an influence on the entire findings of the research.
#2 Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a qualitative data collection method that is commonly utilized in the social and behavioral sciences.
Observation and interviews are being used to gather data, which is then utilized to develop inferences about how society and individuals operate.
Ethnographers study the world as it unfolds rather than attempting to change it in a laboratory.
Due to the obvious unpredictability of life, ethnographers frequently struggle to document their activities in a format that the Board can assess.
#3 Focus groups
A focus group is a small set of precisely chosen people who respond to actual conversations for research purposes.
The hosting organization uses high-quality survey respondents to reflect the larger group they are seeking to reach.
To generalize the response of the population sample, the unit may look at different goods, feature improvements, or other relevant issues.
A facilitator is present during the focus group study. Their role is to assure valid outcomes and to prevent discrimination in conversations.
#4 Grounded theory
Grounded theory is a collection of organized investigative approaches for the inductive approach with the goal of developing theories.
Grounded theory methodological approaches try to generate intermediate ideas straight from data analysis.
The reasoning behind these strategies is based on their inductive theoretical impetus. The power of the resulting analyses is built on convincing grounds.
These analyses offer concentrated, abstract, conceptual hypotheses that describe the actual events under consideration.
#5 Narrative
The narratives have actually been the relevant information in narrative inquiry, which is a type of qualitative research.
Various professions have adopted this method to understand further lifestyle and identity.
#6 Phenomenology
The phenomenological study is a qualitative research approach that tries to comprehend and characterize a phenomenon's fundamental core.
The method explores people's ordinary experiences by deferring the researchers' prior notions about events.
Phenomenological research investigates personal experiences in order to acquire a better understanding of how individuals interpret such experiences.
The Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Data
The key difference between quantitative and qualitative data are not against each other. After all, both are data together.
Quantitative and qualitative data are the key elements of data analysis.
- Qualitative data develops an understanding of human and social sciences to find the way people think and feel, whereas quantitative data generates numerical data and hard facts by employing statistical, logical, and mathematical techniques.
- Qualitative data is holistic, whereas quantitative data is Particularistic
- Qualitative is subjective, whereas quantitative is Objective
- Qualitative data is exploratory, whereas quantitative data are Conclusive
- Qualitative data is inductive, whereas quantitative data Deductive
- Qualitative data is verbal, whereas quantitative data is measurable.
- Qualitative data are Process-oriented, whereas quantitative data are Result-oriented
- Qualitative data is generated, whereas quantitative are Tested
- Qualitative data is in words, pictures, and objects, whereas quantitative data are numerical values.
- Qualitative data is generated to explore and discover ideas used in ongoing processes, whereas quantitative data is to examine the cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- Qualitative data is Non-structured techniques like In-depth interviews, group discussions, etc.., whereas quantitative data is structured techniques such as surveys, questionnaires, and observations.
- Qualitative data develops an initial understanding, whereas quantitative data recommends a final course of action
Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Data in Example
Quantitative data example:
- 60 members participated in the event
- 55 members ate the refreshments
- The event cost 10 gallons of juice
- The average age group of the members participating is 28 years old
- Everyone stayed for approximately 2 hours inside the hall
- Every member paid $10 per person. which is $ 600
Quantitative data example:
- All the members were male
- They were all employed as software engineers.
- The event took place in the party-hall
- The members were asked to write a few sentences about their product experiences.
Which Type is Better for Data Analysis?
Both qualitative and quantitative data are the significant type of data in all the data analyses.
Quantitative data is well-structured and transparent. This data is prepared in such a way that it might have been organized, sorted, and searched for.
Unstructured data is qualitative data. This type of data is designed to be subjective, personalized, and tailored.
Everything is permissible. As a result, if qualitative data is the sole data type in the study, it is inferior. It is, nonetheless, useful.
Because quantitative data is more solid, it is commonly used in data analysis. Numbers do not deceive.
However, for comprehensive statistical analysis, combining quantitative and qualitative data produces the best results.
ReplayBird - Driving Revenue and Growth through Actionable Product Insights
ReplayBird is a digital experience analytics platform that offers a comprehensive real-time insights which goes beyond the limitations of traditional web analytics with features such as product analytics, session replay, error analysis, funnel, and path analysis.
With Replaybird, you can capture a complete picture of user behavior, understand their pain points, and improve the overall end-user experience. Session replay feature allows you to watch user sessions in real-time, so you can understand their actions, identify issues and quickly take corrective actions. Error analysis feature helps you identify and resolve javascript errors as they occur, minimizing the negative impact on user experience.
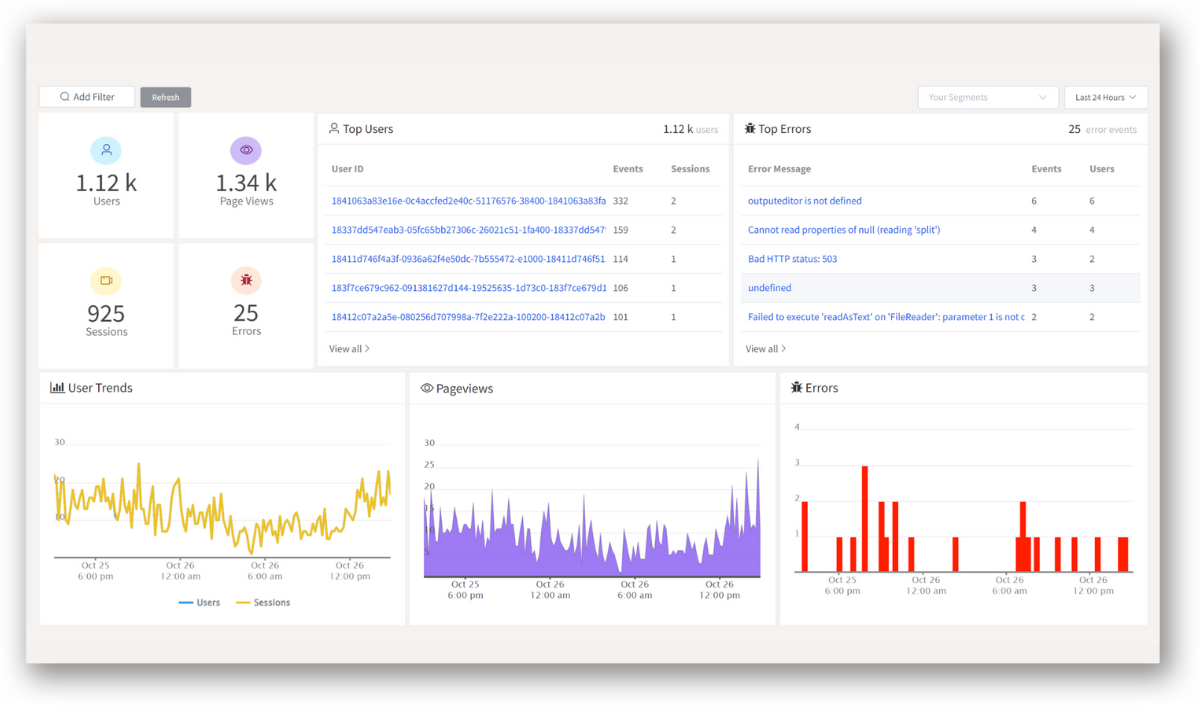
With product analytics feature, you can get deeper insights into how users are interacting with your product and identify opportunities to improve. Drive understanding, action, and trust, leading to improved customer experiences and driving business revenue growth.
Try ReplayBird 14-days free trial
You may also like: